What you need to know about certification ?
30 January 2025
Certification is a compliance tool that allows professionals to communicate on the level of data protection of the products and services they provide.
What is certification?
A certification mechanism allows to establish that a product, service, process or information system has been assessed as compliant with defined criteria. These criteria have been previously approved by the CNIL or the European Data Protection Board (EDPB). The assessment is carried out by an accredited third-party certification body.
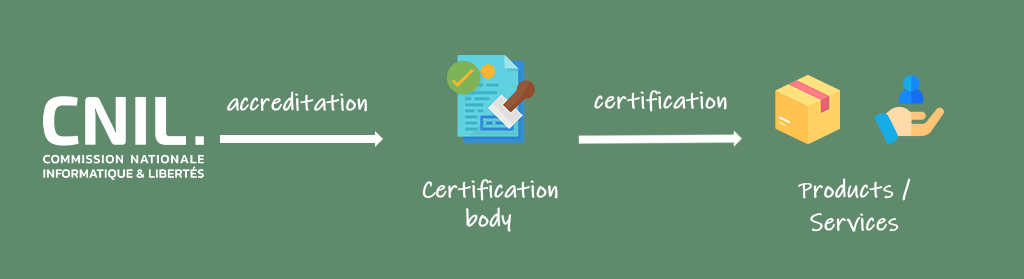
Certification is an tool that enables companies, administrations, associations, and other entities to establish elements demonstrating compliance with the GDPR by adhering to a specific set of criteria. These criteria take into account the obligations of data controllers and processors, and may also include requirements that aim to:
- Promote more data-protective practices;
- Guide professionals in their compliance with the GDPR;
- Ensure consistency between the assessments carried out by different certification bodies;
- Provide more transparency to data subjects.
Similar to code of conduct, certification is a legally binding tool to those who decide to adhere to it. Therefore, the applicant to certification undertakes to:
- Comply with the criteria approved by the CNIL or the EDPB;
- Ensure continuous compliance to these criteria throughout the validity period of the certification;
- Submit to regular audits conducted by the certification body.
Verification of compliance with the certification criteria is systematically carried out from the outset. The certification body will carry out this assessment using a pre-established assessment methodology. At the end of this examination, those who have successfully demonstrated their compliance with the certification criteria will be issued with a certificate.
Who can develop the criteria of a certification mechanism?
There are two possibilities:
- The CNIL can decide to develop the certification criteria;
- The certification criteria can also be developed by a public or private entity that is considered the owner of the certification mechanism. That could be an organisation specialised in personal data protection evaluation, a consumer protection association, a sectoral federation or a body representing groups of data controllers or processors, etc.
In all cases, the certification criteria, including those developed by a private entity, must be approved by the CNIL (or by the EDPB) in order to make it a certification within the meaning of the GDPR or the French Data Protection Act.
In addition, the certification criteria need to be regularly reviewed by the owner in order to take into account, for example, regulatory developments or updates of the state of the art in the IT security domain.
What are the benefits of certification?
Certification allows you to:
- Voluntarily commit to a common set of data protection requirements in a legally binding framework;
- Be able to demonstrate compliance with the GDPR within a specific scope, that of the certification obtained;
- Communicate with the general public and your partners on the basis of a trust label;
- Meet the needs of micro, small and medium-sized companies by promoting the fulfilment of a GDPR compliance process.
What are the differences between a national certification and European certification?
The certifications mentioned in the GDPR or in the French Data Protection Act are subject to approval at national or European level:
- By the CNIL when the certification benefits from a national recognition. Certification mechanisms under the GDPR are also subject to the opinion of the EDPB to ensure the consistent application of the GDPR.
- By the EDPB when the certification benefits from a European recognition. These certification mechanisms are directly applicable in all the member states of the European Union because the specificities of each national law are considered.

